Healthremedy123.com – The surgical repair of tetralogy of Fallot is an effective treatment for this cardiac anomaly. The surgical procedure involves closing the hole in the septum between the two pumping chambers. It can also involve enlarging the pulmonary valve or branches of the pulmonary artery. Although the surgery can cause some complications, the results are long-term. The long-term survival rates of tetralogy of fallot patients are improving.
Tetralogy of Fallot Usually Has Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
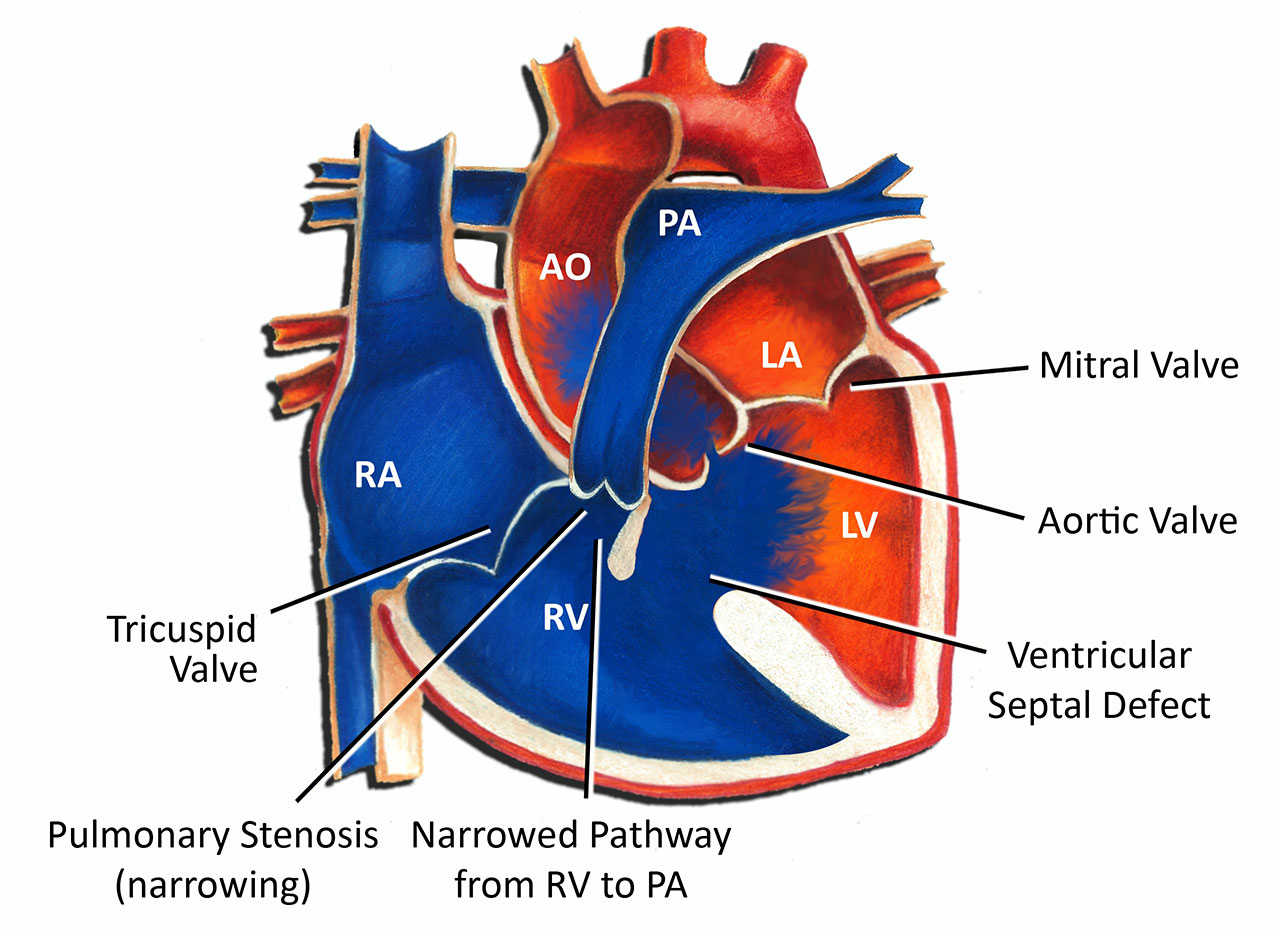
The main artery carrying blood from the heart to the lungs is the aorta. The aorta exits the heart from the left ventricle in a normal heart. Patients with tetralogy of Fallot typically experience pulmonary valve stenosis. Mild stenosis causes minimal cyanosis, while moderate to severe stenosis causes reduced flow of blood to the lungs.
Children with tetralogy of Fallot usually exhibit blue skin and a whooshing sound when the heart beats. A doctor will likely perform cardiac catheterization to evaluate the heart structure and plan surgical treatment. This procedure involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel that guides itself to the heart. A surgeon will insert a stent if necessary. Tetralogy of Fallot surgery can correct the abnormalities in the aorta, preventing the condition from recurring.
While tetralogy of Fallot surgery may be a life-saving option for some patients, late repair of this condition has been associated with a higher risk of ventricular arrhythmias. Late repair has been associated with less right ventricular dilatation, which may explain the high risk of late death. Fortunately, both transatrial VSD closure and cardioverter-defibrillator implantation are associated with reduced ventricular arrhythmias.
The Survival Rate After Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery
The survival rate after tetralogy of fallot surgery is almost equal in patients undergoing a palliative surgery. Compared to patients who undergo primary repair, patients who undergo palliative procedures have similar survival rates. These results, however, should not be considered the only treatment for tetralogy of fallot. The best treatment for tetralogy of Fallot will depend on the patient’s specific medical condition and lifestyle.
While the technical aspects of tetralogy repair are fairly standard, the decision-making process involved with pulmonary valve replacement may be more complicated and have life-altering implications for the patient. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most common surgical options for this condition. The majority of tetralogy repair procedures are performed through open-heart surgery. However, in some cases, patients may require a shunt operation.

Children with cyanotic lesions may be more likely to benefit from non-neonatal repair. Although tetralogy repair is not recommended for neonates, it is possible to delay it until the child is at least 3 months of age. However, it is important to note that if the child is not able to recover from surgery, the procedure may have adverse effects. Depending on the severity of the condition, a second surgery may be necessary to correct the defect.
Postoperative Complications Are Rare
Postoperative complications are uncommon. However, ventricular tachycardia, a life-threatening arrhythmia, may occur. Although this risk is rare, follow-up detection is essential. There is still a residual hole in the ventricular septum after open heart surgery. If this is left uncorrected, the resulting blood flow pattern may result in oxygenated blood flowing to the right side of the heart.
The most common complications after TOF surgery are pulmonary valve replacement and arterial shunt. These complications can cause diastolic dysfunction in the patient. In addition, patients with primary repair may need to undergo mediastinal exploration or aortopulmonary collaterals. A pacemaker is often placed on the postoperative day. It is important to note that the surgical procedure has many risks. This is why primary repair is recommended for neonates with pulmonary artery stenosis.
X-rays can reveal various heart structures. During a cardiac catheterization, a dye is injected through a small tube. This procedure allows the doctor to measure pressure in the heart chambers and oxygen levels in the blood vessels. An echocardiogram, on the other hand, is a more expensive procedure that uses sound waves to create images of the heart in motion. It can highlight the ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, and overriding aorta.
Reference: