Healthremedy123.com – This article will discuss the treatment of Radius Ulna Fracture. The primary goal is to preserve the soft tissue envelope, which optimizes bone healing potential. Failure to maintain the soft tissue envelope adversely impacts periosteal vascularization and depletes the periosteum. This article will examine a number of common surgical techniques for this type of fracture. In addition, we will discuss the role of pain management.
Surgical Resolution of the Fracture
The study described in this article involved a male canine that suffered a high energy trauma from a motorcycle impact. He presented with pain and claudication of his right anterior limb. Surgical resolution of the fracture was achieved using two dynamic compression plates and nine cortical screws. The animal’s prognosis was excellent and he recovered quickly without secondary infections. The authors concluded that the operative approach is best suited for this type of fracture in small breed dogs.
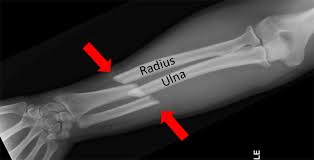
The procedure involves the use of a dynamic compression plate, which has a length of 40 mm, a width of 0.7 mm, and a thickness of 0.2 mm. The plate was then molded to the fracture morphology and secured using Verbrugge reducing forceps. Next, a hole for the proximal end of the clamp was drilled. After the first clamp was secured, an orthopedic drill with a 1.2 mm drill bit and 2.0 guide was used to make holes for the cortical screws.
Safe and Effective Tool for Prying Reduction
A broken radius or ulna bone can cause a deformity of the wrist or forearm. It may cause the forearm to hang or bend away from the other arm. The broken pieces of the bone will also affect the arm’s function, as well as its range of motion. In addition to these deformities, broken bone pieces may result in a shortening or asymmetry of the forearm.

In the majority of cases, prying reduction using mosquito forceps or limited open reduction is an option. In this case, the reduced fracture length is 0.5 cm, the incision is less bloody, and the child may experience some pain after the surgery. Despite the risks, mosquito forceps are a safe, effective tool for prying reduction. The small, blunt tips can minimize the risk of nerve or vascular injuries. This method has several advantages and deserves more clinical promotion.
Undergoing Multiple Procedures to Achieve Reduction
A reduction can be achieved using a closed or open approach. Depending on the location of the fracture, a child may have to undergo several procedures to achieve a satisfactory reduction. The procedure should be performed by an experienced surgeon who is familiar with the area. The LOR technique involves a 0.5 cm incision on the radial side of the distal forearm. A radial artery and abductor longus muscle are separated.
In some cases, the broken bone may tear surrounding nerves and blood vessels. This condition, known as acute compartment syndrome, develops within 24 hours of an injury. This condition causes excessive pain and may limit a patient’s function. Acute compartment syndrome requires immediate surgery. The skin or muscle covering is left open to allow blood to flow to the fracture site. However, if an emergency is not immediate, X-rays may be required.
Reference:


