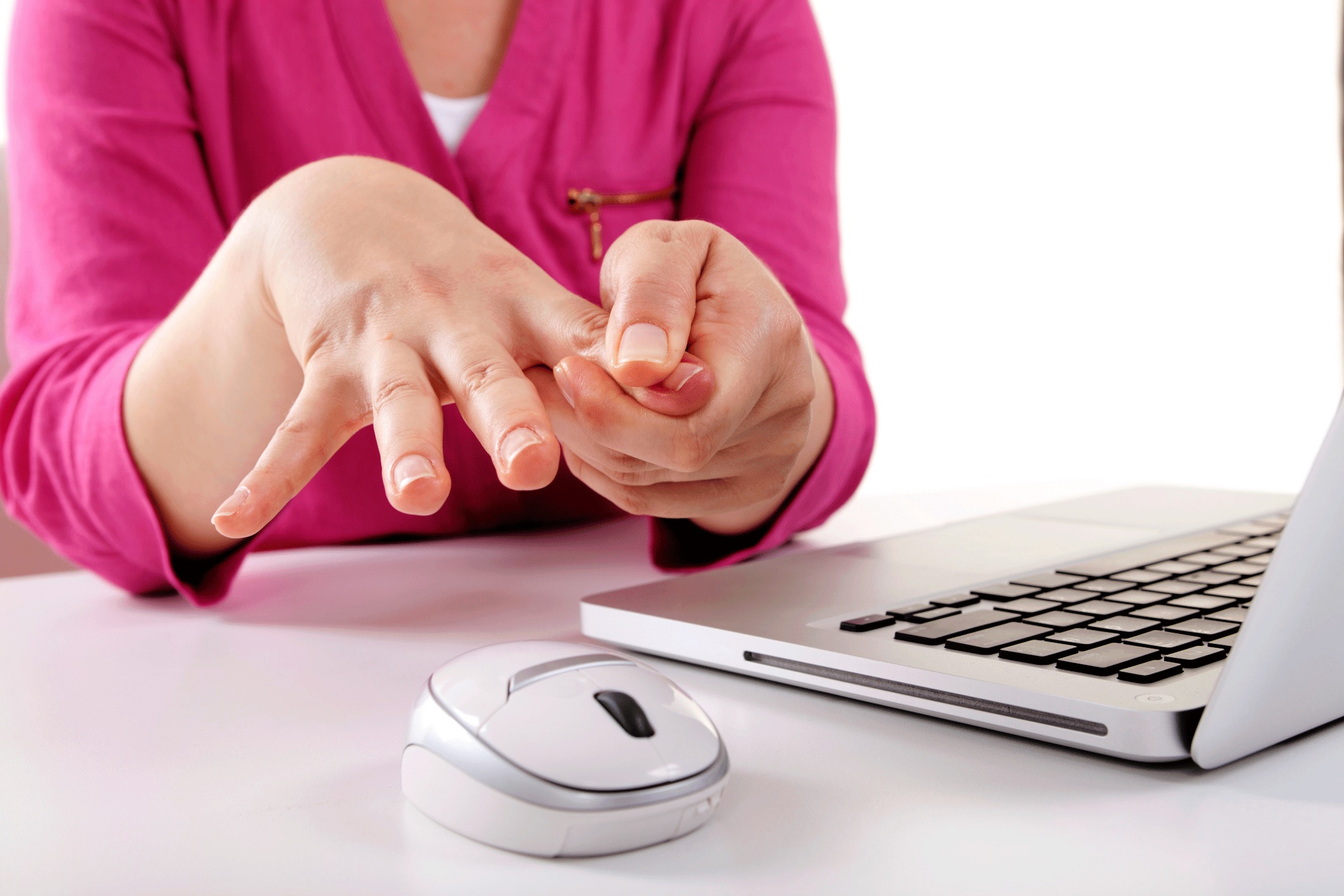
Healthremedy123.com – If you have a painful pinky finger, you may be experiencing the effects of carpal tunnel syndrome. This condition is usually caused by increased pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, which supplies feeling to the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and part of the ring finger. However, the tiny finger is usually unaffected. So, what are the steps to alleviate pain? Keep reading for more information. Listed below are some of the most common causes of pinky finger pain.
The Little Finger has a Peculiar Set up
The pinky finger has a peculiar set-up, referred to as a camptodactyly. In addition, there are two major types of finger bending: clinodactyly and camptodactyly. This deformity is more common in the ulnar side of the hand. If there are two separate abnormalities in the joint, they are called distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ) deformities.
If a tumor is present, it may cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In some cases, bone metastases may cause swelling, pain, or discomfort when pressing the finger. However, in the vast majority of cases, this condition is not serious and does not require medical intervention. Despite the pain, it is important to avoid activities that cause ring finger pain, since the ulnar nerve is located within the pinky joint.

After identifying which joint is affected by fracture, you need to fix its orientation. To fix this, you can use the Components Selection mode or the Select Miscellaneous Components tool icon. Then, select the corresponding index finger and pinky fingers by using the same local direction. Finally, you can apply the various controls to each joint. The next tutorial will discuss the effects of adjusting joint orientations and renaming joints.
Treatment Options Available for Camptodactyly
There are several treatment options available for camptodactyly. Although rare, the disorder affects only one percent of people. Treatment options include stretching, splinting, and surgery. This condition may also be caused by a genetic predisposition. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Fortunately, this type of damage is rare. A doctor can recommend treatments that will relieve pain. While there are many treatments, they may not be enough to correct this deformity.
For more severe cases of clinodactyly, a healthcare provider may recommend reconstructive surgery. Despite the risks, this procedure is not likely to cause any pain or change in your ability to use your fingers. Most cases will not require treatment. However, if the condition continues to worsen, you may need to undergo reconstructive surgery. However, this is only useful in children who are still growing and are at risk for developing bones.
In order to fix the joint, it is necessary to first diagnose the cause of the pain. Then, your doctor can perform an MRI to rule out a more severe problem. This type of surgery may also involve a traumatic injury to the joint, such as a broken bone. In most cases, the joint is healthy, but the doctor can perform a CMC bossing procedure to repair it. However, if you have symptoms, consult your doctor and discuss your treatment options.
Have a Persistent Little Finger Joint Condition
Pain in the joint may indicate that inflammation has occurred in the area. The inflammation that results from this condition will be cured after addressing the underlying condition. In case of persistent pain, you should consult your doctor if your symptoms do not improve after trying over-the-counter treatments. In case of mild injuries, rest and anti-inflammatory medication can be administered. Similarly, buddy-taping may help immobilize your injured finger.
There are several types of treatment for camptodactyly. Surgery is usually necessary if the curve is severe enough and causes problems with function. If your child has mild camptodactyly, a splint may be prescribed to relieve the pain and restore mobility. Occupational therapy may be necessary to prevent further problems. A fusion procedure is necessary in more severe cases. Then, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature.
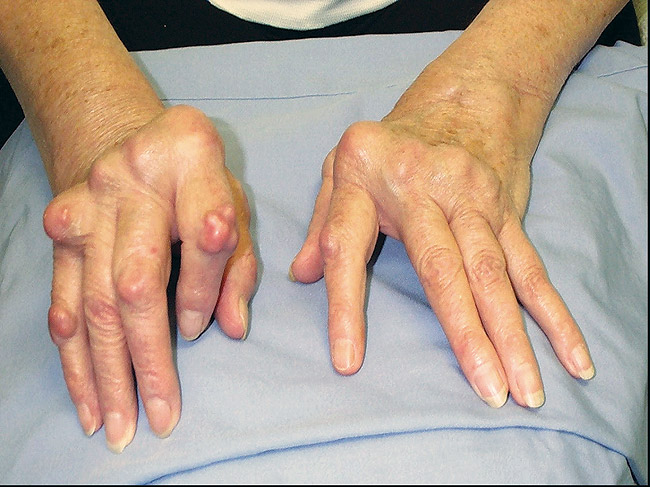
Research suggests that some genetic factors may be involved in developing the disease. An infection may trigger chronic inflammation, and hormones may affect the progression of the disease. Women are more prone to develop this condition than men. Interestingly, the condition improves during pregnancy and may recur after childbirth. Different types of drugs are used to treat pain and slow the progression of the disease. However, the treatment is often inadequate and you should consult a physician if you have a persistent pinky finger joint condition.
Reference:


