Healthremedy123.com – Symptoms of Cerebrovascular Disease include subarachnoid hemorrhage and Ischemic stroke. Treatment options include drugs, surgery, and radiation.
Some Types of Cerebrovascular Disease
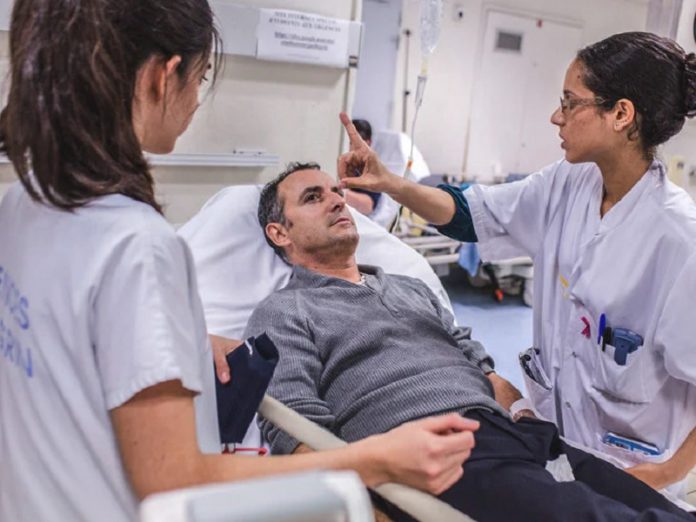
Symptoms of the cerebrovascular disease can be quite serious and can be difficult to diagnose. If you suspect you may have the disease, you should seek medical attention immediately. There are several types of cerebrovascular diseases, including stroke, vascular dementia, and vascular malformations. In addition, the symptoms of the cerebrovascular disease may vary depending on where the blockage is located. For example, a person may have numbness on one side of the body or confusion. Symptoms may also include vision loss, difficulty communicating, or memory problems.
Symptoms of the cerebrovascular disease can lead to a stroke or other brain trauma, which can cause permanent neurological damage. Cerebrovascular diseases are often caused by atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up on the inside of the arteries. These deposits can weaken the artery wall and cause a bulge, which is called an aneurysm. Cerebrovascular disease can also be caused by high blood pressure or uncontrolled diabetes. If these risk factors are not controlled, the person’s chances of developing the disease increase.

Identifying genetic factors related to ischemic stroke can be useful in early identification of high-risk populations and provide novel treatment targets. This study evaluated associations between MMP2 polymorphisms and ischemic stroke. MMP2 is an enzyme that is involved in degrading extracellular matrix (ECM) and inflammatory response. It is encoded by the MMP2 gene and is a calcium-dependent zinc-containing endopeptidase. It may penetrate the basement membrane and degrade elastic fibers, collagen fibers, and other ECMs. It also promotes increased vascular permeability, leading to vasogenic brain edema. Inhibition of MMP2 may have protective effects against atherosclerosis.
Ischemic Stroke is a Complex Disease
Ischemic stroke is a complex disease that involves interactions between genetic and environmental factors. It requires prompt intervention to improve the outlook for the patient. The outlook for cerebrovascular disease depends on the speed at which treatment is implemented. It also depends on the type of event. To identify the genetic factors associated with ischemic stroke, a case-control study was performed. Both healthy controls and ischemic stroke patients were included. All subjects signed informed consent before participating in the study. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 21.0. The association between factors and ischemic stroke was presented as odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
Approximately one in three hemorrhagic strokes are caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage. This condition occurs when the blood in a blood vessel in the brain leaks and causes damage to the surrounding brain cells. These cells may die and cause cognitive disabilities and physical disabilities. The damage to the brain cells can be caused by a ruptured blood vessel, an aneurysm, or a tumor. The amount of damage depends on where the stroke occurred. If the damage is in the brain, it is called an ischemic stroke. If the damage is in the brain and spinal cord, it is called a hemorrhagic stroke.
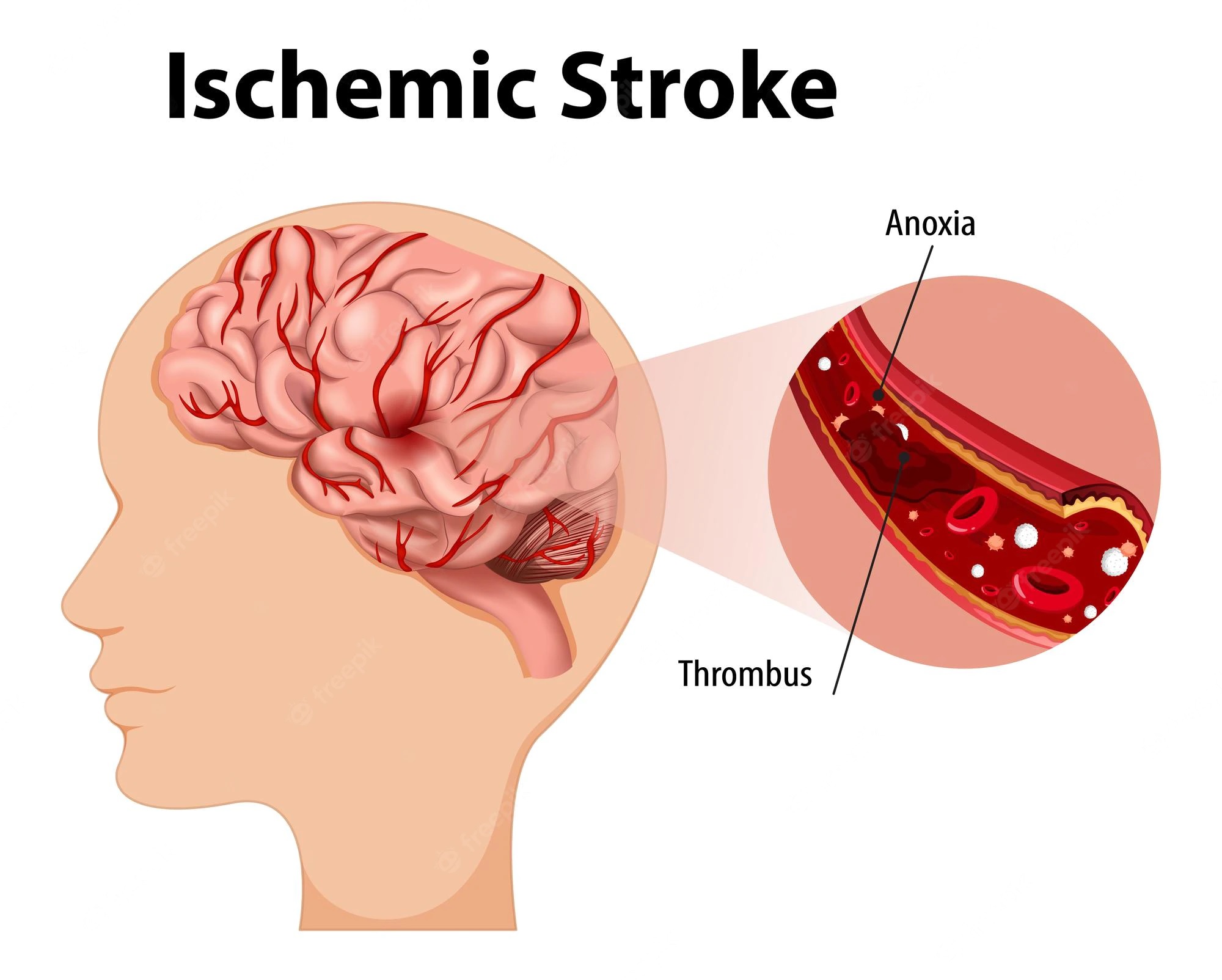
The main symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke include vomiting, headache, and a stiff neck. In addition to these symptoms, you may experience cognitive problems, memory problems, and seizures. These symptoms may be permanent if they are not treated promptly. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately. The most common causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage are a ruptured aneurysm or a hemorrhage caused by a bleed from an arteriovenous malformation (AVM). An AVM is a brain disorder in which the lining of a blood vessel becomes enlarged. A ruptured AVM can be fatal. It can also cause headaches, seizures, and other problems.
Treatment Options Available for Cerebrovascular Stenosis
Several treatment options are available for cerebrovascular stenosis. This condition involves plaque buildup in the arteries, which leads to the hardening of the arteries and blockage of blood flow. Some of these treatment options involve surgery, while others involve medical treatment. The severity of the condition, and the degree of the blood flow loss, will determine the most appropriate treatment.
Symptomatic cerebrovascular stenosis can be treated with medical management, which involves antiplatelet medication and lifestyle changes. These treatment options may include taking anticoagulation medication, quitting smoking, or exercising more. Medical management may also involve stent implantation to relieve vascular stenosis. Stents are used to restore blood flow to the brain and stimulate vessel intima. Stents can also be used to help prevent clots from forming in the artery.
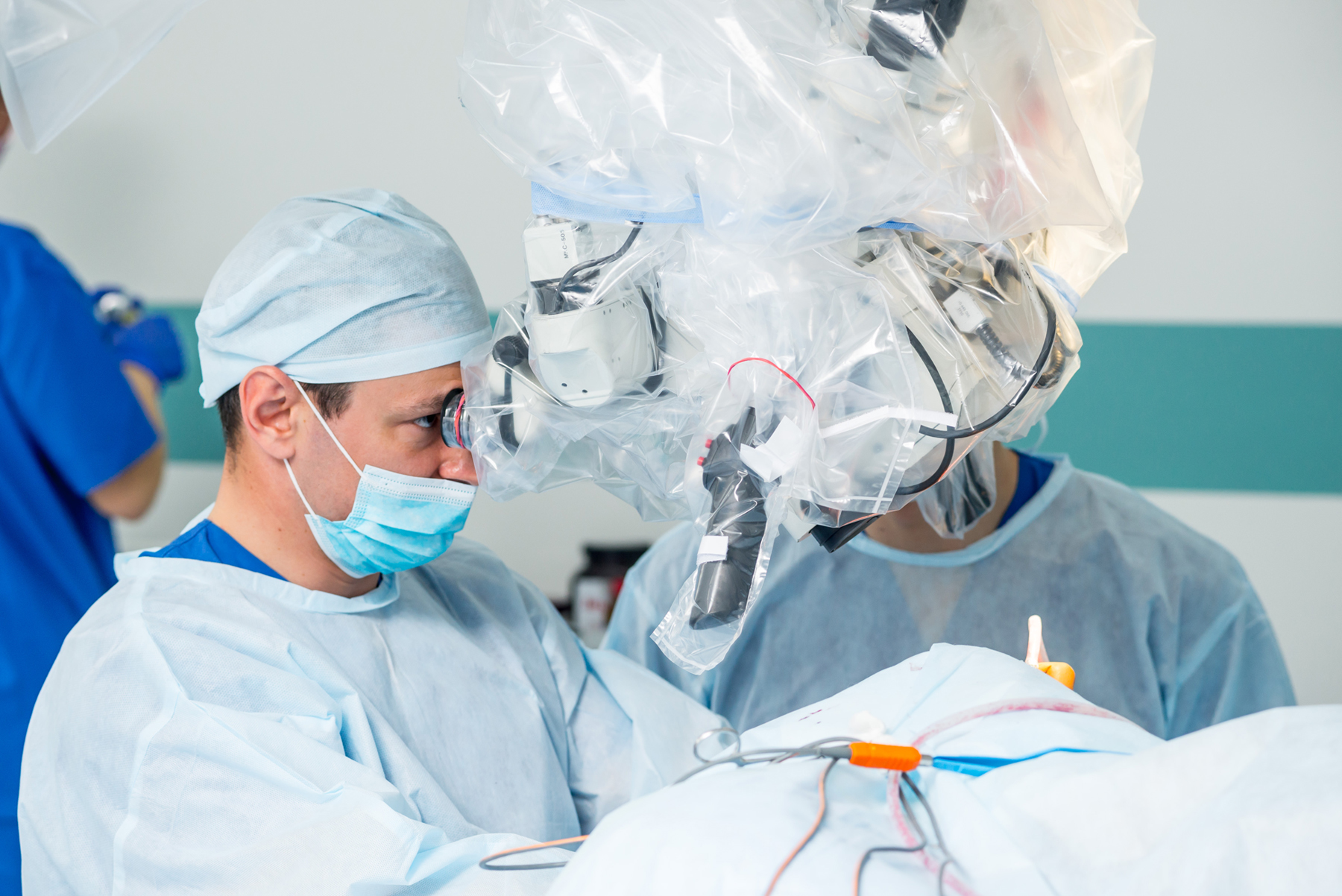
Surgical treatment of cerebrovascular stenosis can involve carotid endarterectomy, which involves opening the carotid artery in the neck. This procedure will help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of a major stroke. It is often recommended for patients with recent symptoms. We really appreciate and welcome guest post submissions from you.
Reference :