Healthremedy123.com – Having a lump on your inner wrist can be quite painful, but there are a number of ways to treat it. For starters, you may want to talk to your doctor about a few simple things you can do to help. These include icing your wrist, applying cold packs, and even taking a bath in warm water. You might also want to try taking a break from work to give your wrist some time to heal.
Ganglion Cysts Are Not Cancerous
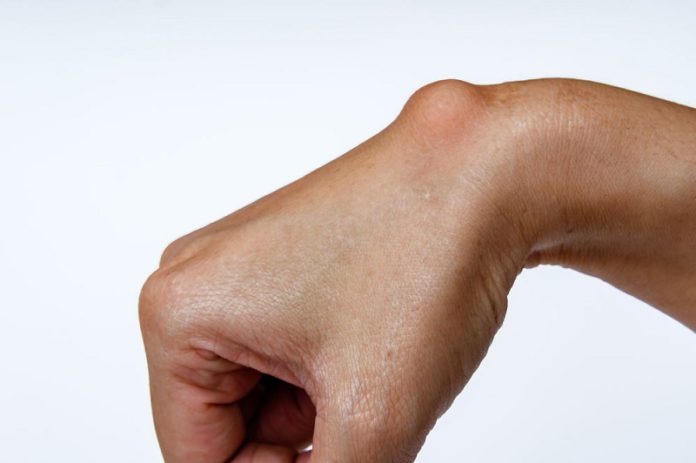
Despite their name, ganglion cysts are not cancerous. They are round or oval lumps that form on the skin, most commonly on the hand or wrist. They may cause discomfort and tingling, but are generally harmless. Usually, ganglion cysts go away on their own. However, if they become painful, they may require surgery. They are most common on the hand or wrist but can be found on other body parts as well.
They are oval, round, or soft lumps that are usually less than an inch in size. They are filled with clear fluid. Ganglion cysts can be caused by overuse, injury, or arthritis. Ganglion cysts are generally noncancerous and can appear in both sexes. They may be painful when pressing against nearby nerves, ligaments, or arteries. They can also cause muscle weakness or numbness.
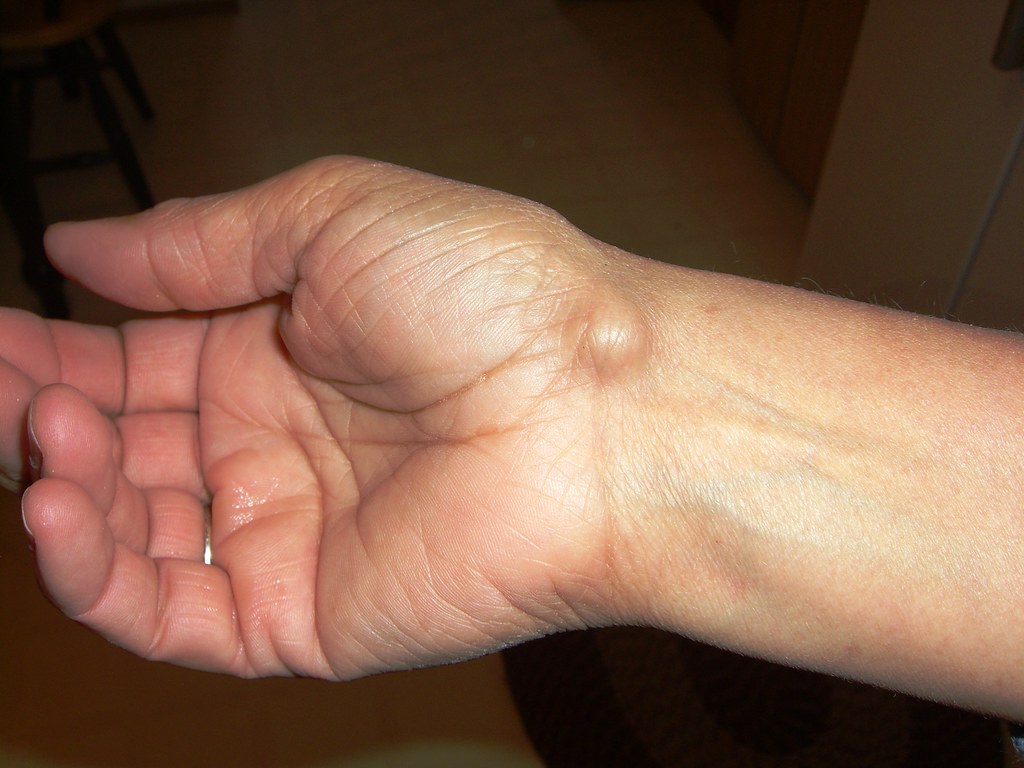
Approximately 1 in 1 million adults develop giant cell tumors of bone (GCTB) during their lifetime. These tumors are benign and rarely spread to other parts of the body. However, they can damage bones and other tissue and cause pain. These tumors are most common in long bones and in the tibia, femur, and hip. Symptoms include swelling, catching sensations when moving, pain, and stiffness. In the UK, primary bone tumors affect approximately 611 people per year. Giant cell tumors of bone account for approximately 5% of all primary bone tumors. They are diagnosed and treated with surgical resection. They can also be treated with radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
Giant Cell Tumors Are Benign Tumors
Giant cell tumors are typically benign tumors, but they can cause damage to bones and other tissue. In some cases, the tumors can grow quickly. In other cases, the tumors may be small and painless. However, in larger tumors, pain may be present and the tumor may require surgery. Usually asymptomatic, Epidermal inclusion cysts can become infected or inflamed. If they do become infected, they can be treated with antibiotics. They can also be removed.
Symptoms include a dome-shaped lump that can be painful, swollen, or inflamed. It may be located on the inner wrist, neck, and back. They can also occur on the face, chest, and legs. Depending on their location, they may be minor or more serious. If you notice a lump on the skin, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist or plastic surgeon. These professionals can help diagnose and treat epidermal inclusion cysts. They may order imaging, drain the cyst, or refer you to a general surgeon.
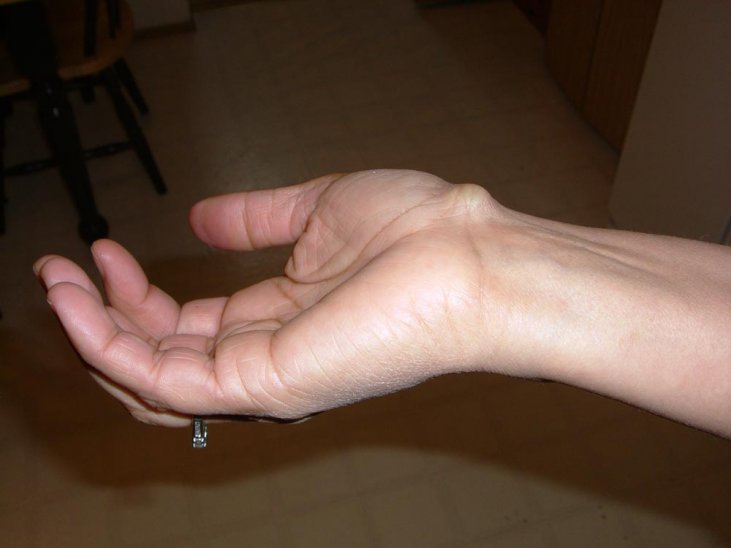
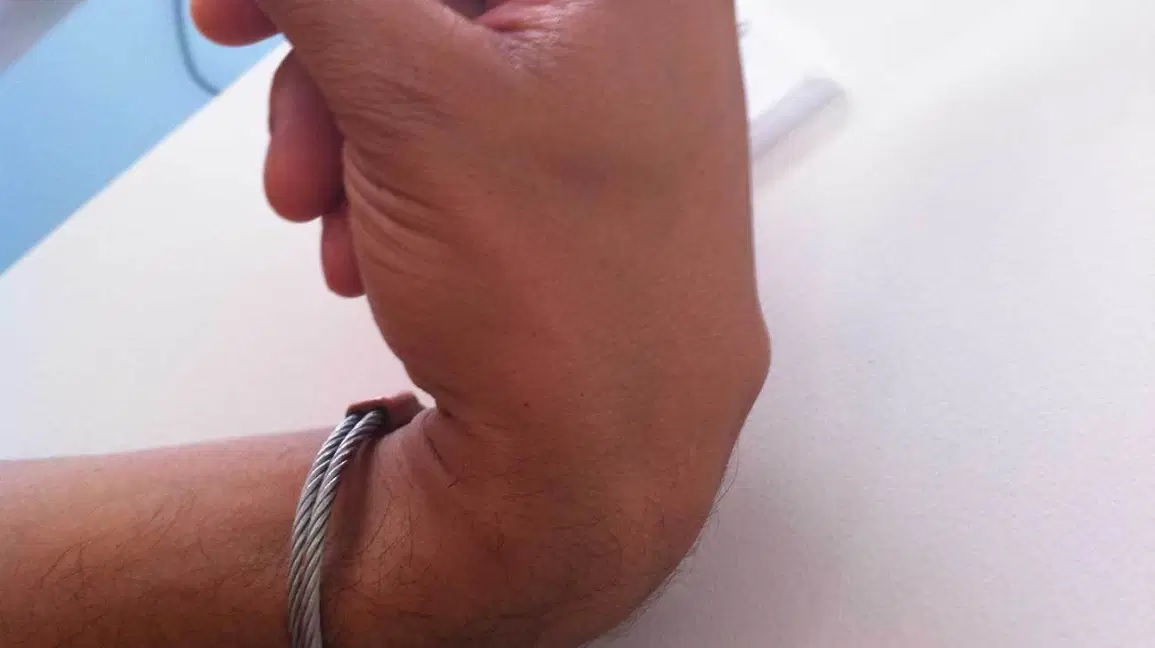
Most epidermal inclusion cysts occur on the back and neck, but they can occur anywhere. They are usually asymptomatic, but they can become infected and painful. When they become infected, the skin around them becomes red and inflamed. In addition, they may become painful when you brush your hair or wear a seatbelt. Those who suffer from the carpal boss on the inner wrist may experience a painful bump that causes discomfort when the wrist is bent. This condition is related to a number of congenital issues, joint trauma, and overuse. If you have a painful bump on your wrist, you should contact a hand and wrist specialist in Atlanta to explore your options.
Carpal Bossing was Diagnosed by Physical Examination
The Carpal boss is a bony protuberance located at the junction of the carpal and metacarpal bones. Most people who have the condition do not experience serious pain. However, the bump can interfere with daily activities. Carpal bossing is usually diagnosed by a physical exam. Your doctor will evaluate your range of motion and determine when you first noticed the bump. They will also check your wrist’s strength. They may also test your wrist to see if the bump is causing pain.
Often, people are self-conscious about the appearance of a lump on the inner wrist ganglia. The lump, also called a ganglion, is not cancerous. But it can cause pain, discomfort, and other problems. Ganglions are fluid-filled sacs that can form on the hands, feet, ankles, and wrists. They are caused by injury or overuse of a joint. They can cause a lot of pain and can interfere with movement. However, most people who have ganglions don’t require surgery.
X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI can help detect ganglions. They also help to determine the cause of the cyst. Ganglions that don’t go away after 6 months may cause functional problems. In addition to causing pain, ganglions can affect your range of motion. They can also cause numbness and weakness. They can appear anywhere on the hand but are most common on the back of the wrist.
Reference: