Healthremedy123.com – Using the elbow as a tool to move your hand is one of the best ways to get a good workout. It is a great way to get in shape and it can help you keep your weight off. Using your elbow can also prevent injuries from occurring, such as sprains and strains. Symptoms of a distal triceps rupture include pain at the front of the elbow, swelling, bruising, and a popping sound. It is important to get medical help as soon as possible. The injury will not heal on its own, and surgery is required.
Distal Triceps Rupture Occurs in Men Over the Age of 30
Distal triceps ruptures are rare, but they are common in men over the age of 30. They are also more common in male athletes who use anabolic steroids. Often, the tear is caused by a blunt force on the elbow. The biceps is a large muscle that extends from the shoulder joint to the elbow. It participates in elbow flexion, supination, and extension. A distal biceps tear can cause difficulty in turning the palm up or down, and weakness in supination.
Symptoms of medial epicondylitis in the elbow front usually start with gradual onset of elbow pain. The pain typically radiates from the front of the elbow to the wrist. In some cases, the pain also may be felt in the inner elbow. The pain may be worse during activity, such as during the cocking phase of a sport. Medial epicondylitis in the elbow is caused by the overuse of the tendons of the elbow. Repetitive wrist flexion activities, such as tennis racket squeezing or lifting, can put stress on the tendons and lead to pain.

The pain may be relieved by icing the affected area, resting, or limiting the use of the affected arm. If the pain is persistent, a doctor may recommend surgery to correct the condition. The surgery may involve arthroscopic or arthroscopically-assisted techniques. The surgery may involve the removal of damaged tissue, the removal of extra bone, or the removal of a buildup of scar tissue.
Exercises to Build Forearm Strength
Often neglected, the forearm is an essential muscle group. It plays an important role in many activities. It controls your grip, allows you to move your fingers, and contributes to big movements. There are many exercises for building forearm strength. These include barbells, dumbbells, resistance bands, and free weights. If you have limited mobility, you may want to consult a therapist to develop a program for you.
Strengthening the muscles in your forearm can help you to pick up children, carry groceries, or push vacuums. Keeping them strong can also prevent injury. Those who are interested in building their forearm muscles can use free weights, resistance bands, and other forms of resistance training. The length of the muscles in your forearm is influenced by your genetics. Various ligaments work together to hold the elbow joint together. The elbow is a hinge joint that allows the forearm to bend, twist, and rotate. It is made up of three bones, the humerus, ulna, and radius. All of these bones are covered with cartilage that absorbs shock and provides a smooth surface for the elbow joint.

The elbow joint is composed of articular cartilage that covers the ends of the bones. The humerus and ulna are connected by the triceps tendon. The elbow is also surrounded by a joint capsule, which provides lubrication and stability. The joint capsule is lined with synovial fluid, which acts as a cushion to reduce friction between the bones. The elbow joint capsule is strengthened by medial and lateral ligaments. These ligaments hold the tendons in place. Injuries to the lateral collateral ligament can cause the elbow to become unstable. If the ligament is torn, it can be repaired with sutures. The healthcare provider may place the elbow in a splint to stabilize the joint.
Surgery to Reduce Pressure on the Nerves
Located on the back of the forearm, the ulnar nerve supplies sensation and movement to the arm. It is part of the peripheral nervous system, which sends messages to the brain from the lower limbs. If the nerve becomes injured or compressed, it can result in pain, numbness, or other symptoms. The ulnar nerve can become trapped in the cubital tunnel, which is a passageway underneath the medial epicondyle of the elbow. In addition to causing arm pain, it can cause numbness in the fingers. It may also result in weakness in the ring and pinky fingers. If the nerve is severely damaged, it may be necessary to undergo surgery to relieve pressure on the nerve.
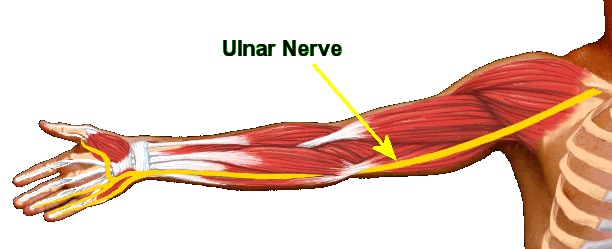
Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most common peripheral nerve entrapment syndrome. It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve, which can be caused by a number of factors. Some common causes of compression include prolonged elbow flexion, repetitive movement of the arm, and daily habits.
Reference:


